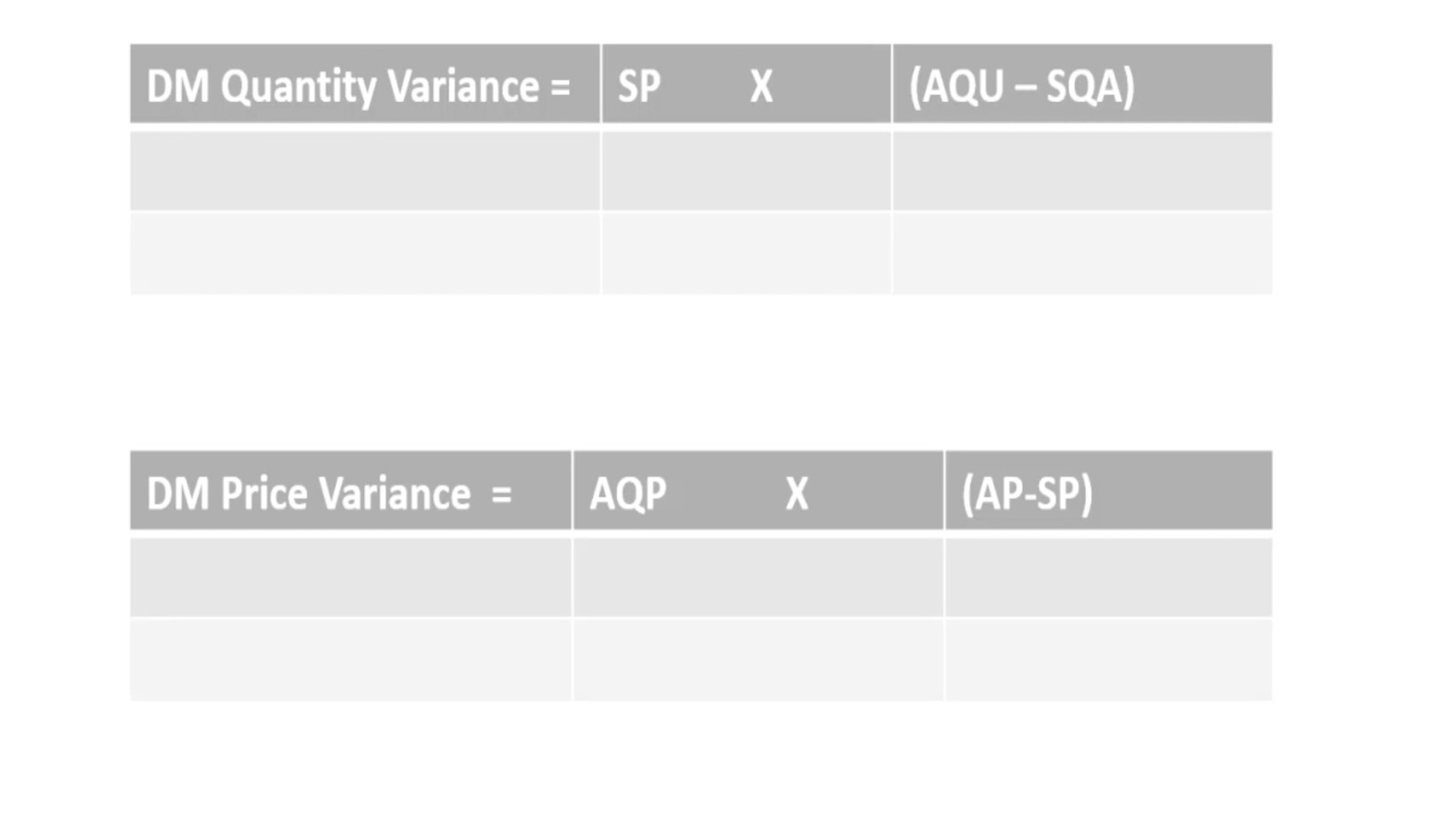
Understanding Materials Quantity Variance
Materials Quantity Variance is a metric used in cost accounting to measure the difference between the standard quantity of materials that should have been used in production and the actual quantity used. It helps businesses analyze the efficiency of their material usage and identify any deviations from the expected standards.
When the actual quantity used is higher than the standard quantity, it results in an unfavorable materials quantity variance. This indicates that more materials were used than planned, leading to increased costs. On the other hand, when the actual quantity used is lower than the standard quantity, it results in a favorable materials quantity variance, indicating potential cost savings. Several factors can contribute to materials quantity variance:
- Poor inventory management: Inaccurate tracking of inventory levels can lead to overstocking or understocking of materials. Overstocking can result in increased materials usage, leading to an unfavorable variance. Understocking, on the other hand, can cause production delays and inefficiencies.
- Inaccurate forecasting: Incorrect estimation of material requirements can result in either excess or insufficient materials usage. This can lead to unfavorable variances and impact the overall production process.
- Inefficient production methods: Inefficient production processes can result in material wastage or excessive usage. This can be due to factors such as inadequate training, improper equipment, or ineffective production planning.
- Supplier issues: Problems with suppliers, such as late deliveries or poor quality materials, can impact the materials quantity variance. Delays in receiving materials can disrupt production schedules, while poor quality materials may require additional quantities to meet the desired product specifications.
By understanding these factors, businesses can take proactive measures to address them and optimize their material usage. This can include implementing better inventory management systems, improving forecasting techniques, optimizing production methods, and establishing strong supplier relationships.

Importance of Monitoring Materials Quantity Variance
Monitoring materials quantity variance is crucial for businesses to understand the cost implications associated with it. Unfavorable materials quantity variance can result in increased costs and reduced profitability. By keeping a close eye on this variance, companies can identify and address any inefficiencies in their production processes.
When materials quantity variance is unfavorable, it means that more materials were used than what was expected or budgeted for. This can lead to higher costs due to the additional materials needed to complete production. These increased costs can have a significant impact on a company’s bottom line, affecting its overall financial performance.
Unfavorable materials quantity variance can also indicate inefficiencies in a company’s production process. If more materials are being used than necessary, it suggests that there may be wastage or inefficient utilization of resources. This can result in longer production times, decreased productivity, and higher labor costs.
An Unfavorable Materials Quantity Variance Indicates That
One of the main causes of unfavorable materials quantity variance is inaccurate inventory management. When businesses don’t have a clear understanding of their inventory levels, they may end up over ordering or under ordering materials. Overordering can lead to excess inventory, which ties up capital and increases storage costs. On the other hand, underordering can result in production delays and missed opportunities. By implementing efficient inventory management systems and regularly monitoring stock levels, businesses can reduce the risk of unfavorable materials quantity variance.
Another factor that contributes to unfavorable materials quantity variance is poor quality control. When materials are of subpar quality, they may not meet the required specifications, resulting in increased waste and rework. This can lead to higher material usage and ultimately contribute to unfavorable variance. By implementing strict quality control measures, conducting regular inspections, and working closely with suppliers to ensure consistent material quality, businesses can minimize the risk of unfavorable materials quantity variance.
Inefficient production processes can also lead to unfavorable materials quantity variance. When production methods are not optimized, there is a higher likelihood of material waste and inefficient resource allocation. This can result in overconsumption of materials, leading to unfavorable variance. By analyzing and optimizing production processes, businesses can identify opportunities for improvement, streamline operations, and reduce materials waste, ultimately minimizing unfavorable variance.
By addressing these root causes of unfavorable materials quantity variance, businesses can improve their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance their financial performance. Implementing accurate inventory management systems, ensuring strict quality control measures, and optimizing production processes are essential steps towards preventing ongoing cost overruns and maintaining a competitive advantage.