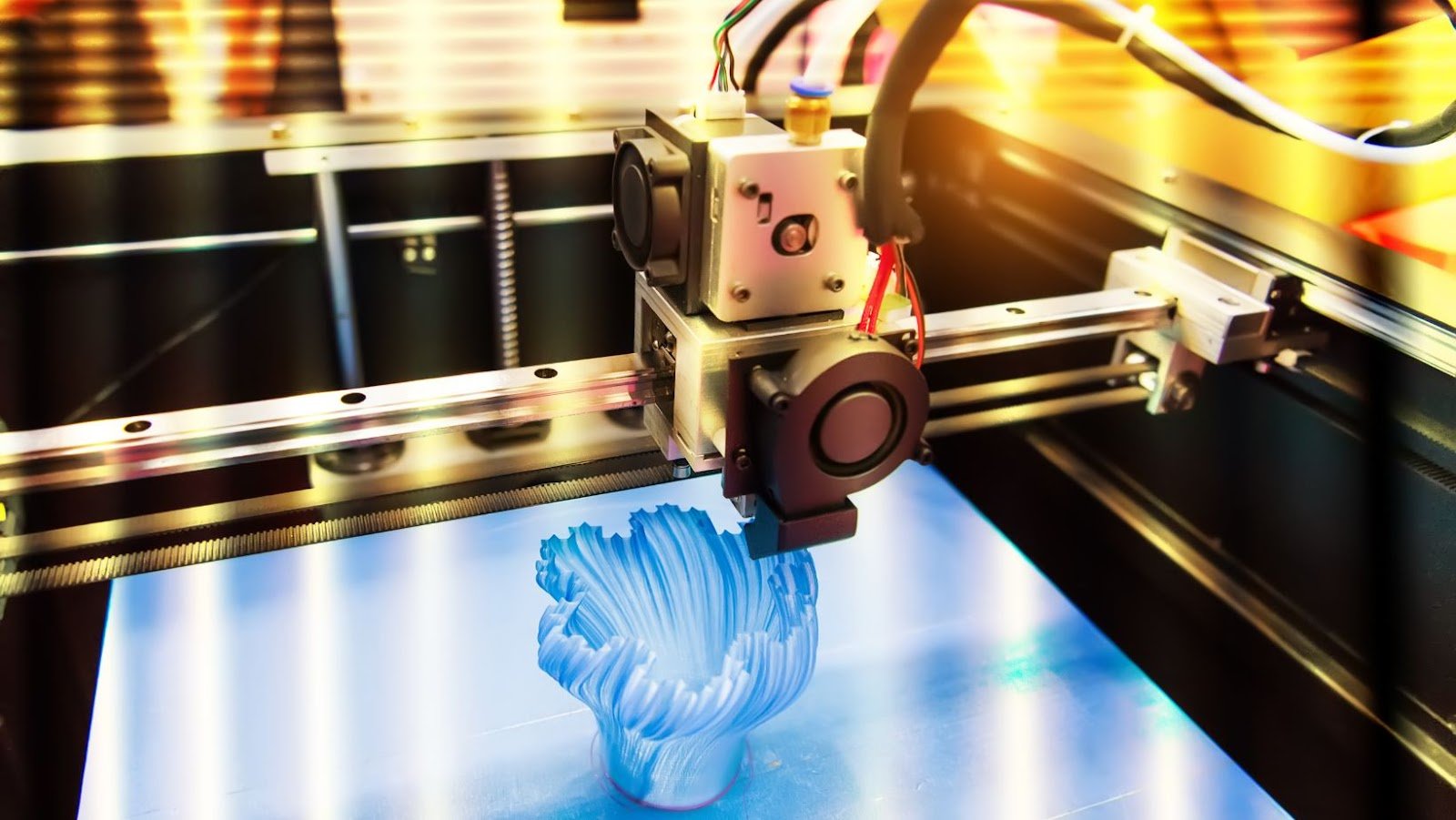
The history of 3D printing can be traced back to the 1970s when Chuck Hull invented stereolithography, a process for creating three-dimensional objects by using a laser to draw them onto a photosensitive resin. Hull then founded 3D Systems, which is now one of the largest 3D printing companies in the world. In the 1980s, another important 3D printing technology was developed: selective laser sintering (SLS), in which a laser is used to fuse small particles of powder into a solid object. SLS was invented by Carl Deckard and Joe Beaman at the University of Texas at Austin. In the 1990s, 3D printing began to take off, with the development of the first commercial 3D printer, the Z Corporation ZPrinter, in 1993. Since then, the technology has continued to evolve and advance, with ever-more sophisticated 3D printers being developed for both commercial and home use. Today, 3D printing is used in a wide range of industries, from aerospace to healthcare, and is revolutionizing the way that products are designed and manufactured.

In recent years, 3D printing has become increasingly popular in the medical field. This technology can be used to create custom prosthetic limbs, implants, and even human tissue. 3D printing is revolutionizing medicine and giving hope to patients who otherwise would have none. One of the most amazing things about 3D printing is that it can be used to create custom-fit implants. This is especially helpful for patients who have unique body shapes or who have lost a limb. 3D printing can also be used to create human tissue, which can be used to repair damaged organs or test new drugs. It has the potential to change medicine forever and save countless lives.
Nevertheless, 3D printing has several disadvantages when compared to traditional manufacturing methods. These include:
1. Limited material options: 3D printing is currently limited to a small number of materials, including plastic, metal, and glass. This limits its use for many applications.
2. High cost: 3D printers are still relatively expensive, and the cost of materials is also high. This makes 3D printing a less viable option for mass production.
3. Slow speed: 3D printing is a slow process, and it can take hours or even days to print a single object. This limits its use for applications where speed is of the essence.
4. Poor surface finish: 3D printed objects can have a rough surface finish, and this can be a problem for applications where a smooth finish is required.
5. Accuracy issues: 3D printers are not yet capable of printing objects with the same level of accuracy as traditional manufacturing methods. This can be a problem for applications where precise tolerances are required.
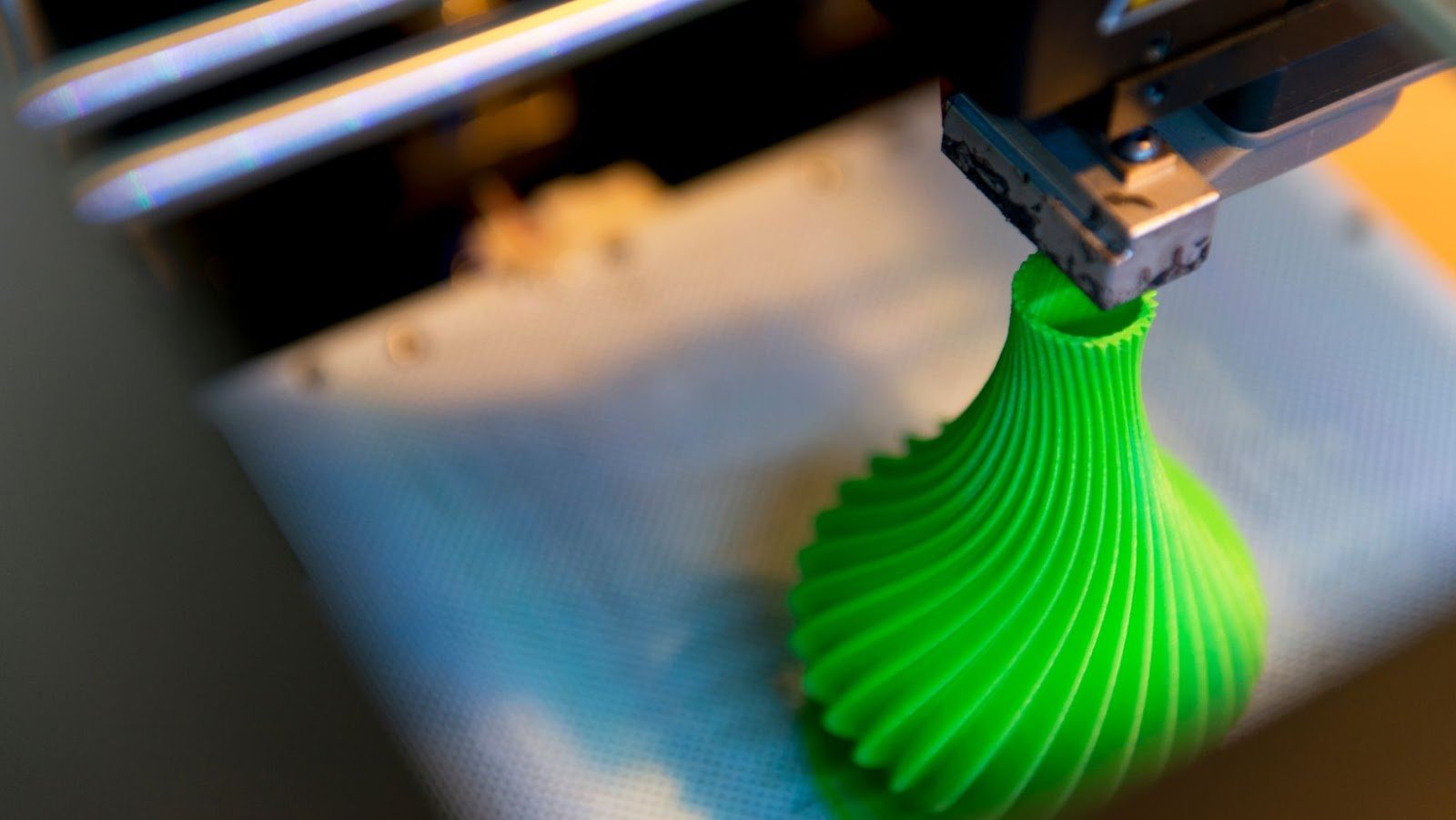

In conclusion, 3D printing technology is constantly evolving and becoming more and more advanced, just like Tonybet. Every day, new and innovative 3D printers are being developed that are capable of printing even more intricate and detailed items. As technology progresses, 3D printers are becoming smaller, cheaper, and more widely available, making them more accessible to everyone. One of the most exciting recent developments in 3D printing is the ability to print using multiple materials. This means that, for the first time, it is possible to print items that are made up of multiple different colors or even made of different materials altogether. This opens up a whole new world of possibilities for what can be created with a 3D printer. Another exciting development is the ability to print in metal. This is a game-changer for the 3D printing industry, as it opens up the possibility of printing functional metal parts and products. This could have a huge impact on manufacturing and could lead to metal 3D printing becoming the norm. Overall, it is clear that 3D printing technology is progressing at a rapid pace and is becoming more and more advanced. Every day, new and exciting developments are being made that are pushing the boundaries of what is possible.