Each new iteration of the Android operating system brings with it more and more control powers for end users. This is always welcome and we definitely need more control over our data, location tracking and privacy in general. Android 11 is no exception to the rule, as it brings valuable improvements. Here’s what’s new and how to manage the rights on Android 11.
How do I check Android authorizations?
The resolutions remain the same, so there are some minor changes. Android 10 has been a big leap forward. In particular, many applications do not have access to all your local files, but only to your media files. Or by adding a separate option Privacy in the main settings menu.
So, as with Android 10, instead of the default options for authorization and denial, Android 11 generally gives 3 options for most authorizations. What you see are these three:
- Allow only while using the application – The application only has access to z. B. Camera or location when you are actively using it.
- Ask Every Time – You will be notified each time access is granted or denied when certain privileges are granted.
- Refusal is self-explanatory, synonymous with you will not pass!
That’s great, especially to address the problem of privacy being invaded by applications that track your location, even if you don’t need them. Of course, if authorisation requires background access or permanent access (such as access to contacts), you must always choose between authorisation and denial.
This also does not apply to Google’s services, as they have access to most functions by default. The benefits of working for Google, I suppose. To view them, you need to go to your Google Account here. Here you can disable various things as part of the activity checks, such as B. site history, which uses your location in the background.
We’ll give you an example. Suppose you want to check which application has access to your files and media (storage access). That’s what you’d do:
- Open the settings.
- Open secrecy.
- Press the authorization manager.
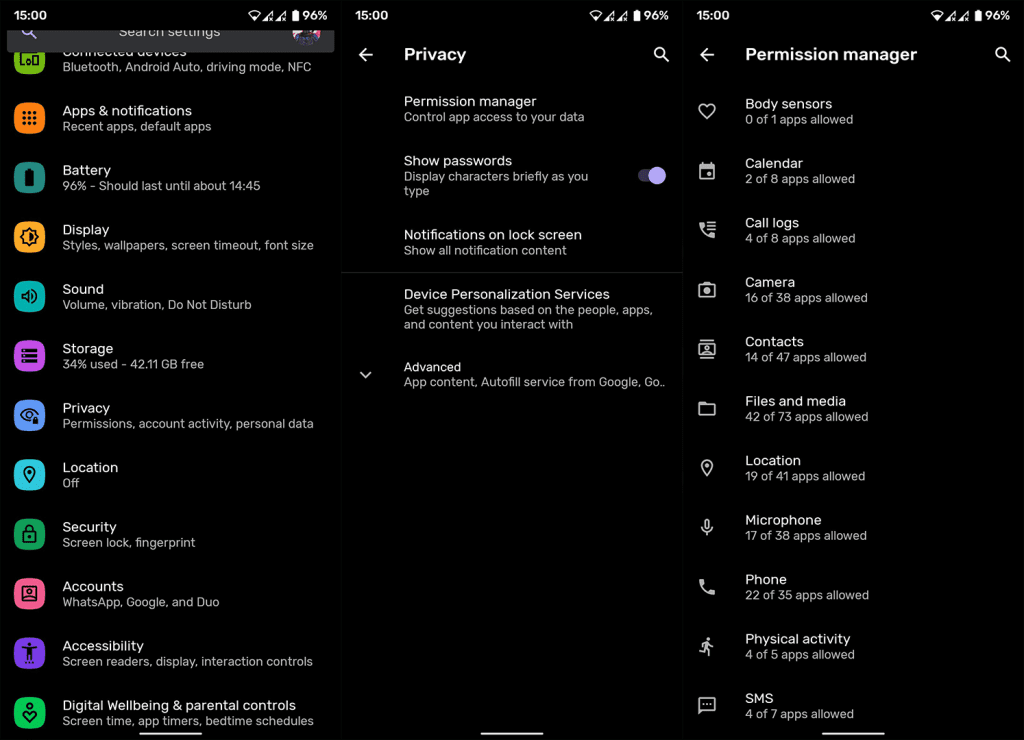
- Open files and media.
You can see which application has access to your storage space, which only has access to media and which has no access at all. Of course, for obvious reasons, file managers have full access to all files.
Special permits and where to find them
Special permissions or access to special requests are things you’ll rarely see, and few requests ask for them. These include image-in-image functionality, access to notifications, unlimited use of data, installation of unknown applications (for more information on this resolution, click here), and some others. You can manage these rights on Android 11 as you would on Android 10.
You need to manually access specific applications in the settings. It’s less likely that you would accidentally allow an application to, say. B. to take control of the Wi-Fi. Because of their permanent nature, you can only allow or deny access.
Some applications, like. B. Custom launchers, require access to notifications or even the device management application. This is not a normal authorization and is available under Settings > Security > Device management applications.
Application-specific access can be found under Apps and Notifications in Settings. Learn here how to find it and how to configure special rights:
- Open the settings.
- Select Applications and Communications.
- Work it out.
- Free access to specific applications.

- Select a category and a list of requests that have been granted or refused.
For a detailed explanation of what a certain resolution is, open any application in the list and you will see an explanation under the button.
New function: Delete permits if the application is not used
And in addition to the migrated enhancements of Android 10, there is a very useful and practical addition to Android 11.
There is an option in the application’s authorization settings that allows the system to remove authorizations when an application is not used for a longer period of time.
That’s great, especially for users who store a lot of applications and don’t use them very often. If you want to try it out in individual applications, you can find it here:
- Open the settings and
- Then tap Calls and Notifications.
- Press All Applications.
- Open the application you want to restrict if you do not use it.
- Click on Permission.
- Enable the Remove permissions option when the application is not in use.

The next time you open the request, you will be asked for permission again.
And as far as that’s concerned, we can close this article. Thanks for reading and don’t forget to visit our Facebook and Twitter pages for more informative articles.
Related Tags:
one-time permission android,android 11 location permission example,android 10 permissions programmatically,grant permission android,android 11 location permission,android 11 background location permission,android 11 auto revoke permissions,android 11 scoped storage,android 11 features,android app permissions list,android permissions list,app permission setting,android app permissions manager,app permissions android,android app permissions explained,android app permissions developer,android app restart when change permission










































































































